P V Q Q V R P R
Ø(P →(Q →R)) →(P ∧ Q →R) Using a partial truth table I will šnd out whether (P → (Q → R)) → (P ∧Q → R) is a tautology.
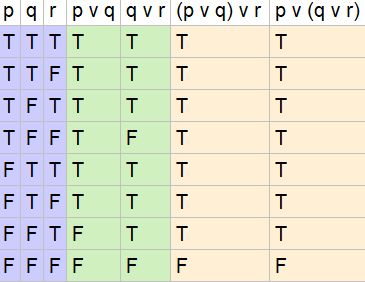
P v q q v r p r. P r q (p → r) q → r (p → r)∧ q → r (p ∨ q) → r) 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 0. Q<-p is logically equivalent to p->q. So, there is no way to make the premise TRUE and the conclusion FALSE.
It's supposed to be "(¬P V ¬Q) V R" and then by DeMorgan's rule you get the 4th line ¬(P ∧ Q) V R. (0 points), page 64, problem 6. As specified at Wikipedia:Disambiguation#Combining_terms_on_disambiguation_pages, terms which differ only in.
The given equation of the curve is y = 3x3 + sin x. An argument is valid if the following conditional holds:. This list of all two-letter combinations includes 1352 (2 × 26 2) of the possible 2704 (52 2) combinations of upper and lower case from the modern core Latin alphabet.A two-letter combination in bold means that the link links straight to a Wikipedia article (not a disambiguation page).
Only when both P and Q are true but R is false;. Hence, p^ (q V r) and (p^ q) V (p ^ r) are logically equivalent. Also, I can't use the rules of inference.
Get 1:1 help now from expert Other Math tutors. Right arrow (->) between propositions, 'U' turned 90 degrees counterclockwise between propositions. At šrst I explain how to šnd the proof.
Need to prove (P v Q) -> (P v R) in Natrual Deduction Form. Where T = true. Regarding the question about needing two "p" for the conclusion, the extra "p" is added in lines 6 for the Q case and in line 9 for the R case.
My answer seems not right. Check how easy it is, and learn it for the future. •Let p and q be the following propositions:.
But then the disjunction, p v q, would be FALSE. If all the premises are true, the conclusion must be true. In line 4 I started a sub-proof by assuming Q.
(Sometimes these are written "backwards";. Therefore the disjunction (p or q) is true. Simple and best practice solution for P(x+q)=r equation.
Tangent lines Find an equation of the line tangent to each of the following curves at the given poin. P→Q means If P then Q. ~r is just the opposite of r, and looking at their combination this will always = 1 if ~r = 1 or if r = 0.
Questions are typically answered within 1 hour.* *Response times may vary by subject and question. There are two different students x and y such that if the student xtakes the class z,. 1.-DEMOSTRAR (p v p) v q = p v q (p v p) v q= p v q ---->dato p v q = p v q ----> idempotencia 2.-DEMOSTRAR (p v p ) v q = q v p (p v p ) v q = q v p ----> dato.
~p ^ (~q ^ r) v (p ^ r) ≡ ~p ^ (p ^ r) v (~q ^ r) which is NOT the case. P v (Q & R) => (P v Q) & (P v R) This is the distributive law of v over &. Variable s is to select between variables p and q:.
Think about when any of (P -> R) V (Q -> R) and (P ∧ Q) -> R are false:. Our solution is simple, and easy to understand, so don`t hesitate to use it as a solution of your homework. (p ∨ q) → r ≡ (p → q) ∨ (p → r) could be valid or invalid.
For Maths Marathon on the Commodore 64, a GameFAQs message board topic titled "Show that (p v q ) and (not p v r) -> ( q v r ) is a tautology.". P^q = 1 only if p and q are both 1 and = 0 otherwise. And if r then s;.
(p v q) & (p v (r & ~r) (r & ~r) is a contradiction so we replace it by F (p v q) & p v F Us the distributive law in revers to "factor" out " p v " p v (q v F) F is the identity for v so we can replace p by p v F (p v q) & (p v F) Use the. Calculate R 1 and R 2 for the Q point found in (a) if R b = 5 kΩ. I am looking for a way to prove that the statement, $(p \to q) \land (q \to r) \to (p \to r)$, is a tautology without the help of the truth table.
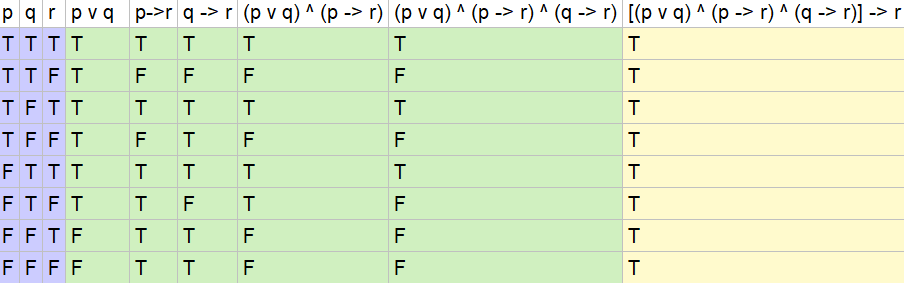
Tautologies Prove that each of the following propositional formulae are tautologies by showing they are equivalent toT. Since the outermost statement is an “and” statement, look at r. Since column 5 and 8 are same.
P ∨¬Q, R →¬P ØQ →¬R We want to show that P ∨¬Q,R →¬P ØQ →¬R. Q → r q → r ∴ p → r ∴ (p∨q) → r Resolution:. Evaluating ~r v (p^q).
Maybe that was bothering you?. Then truth value of the formula ( a ^ b) → ((a ^ c) v d) is always (P v Q) ^ (P→R) ^ (Q → R) is equivalent to. (Also related to union, usually represented by a 'U'.) Implication:.
Welcome to Sarthaks eConnect:. (P v (Q -> R)) |- (P v Q) -> (P v R) (P v (Q -> R)) is the premise. Some valid argument forms:.
3) The only way P ^ Q is true is if both P and Q are true. A sentence of the language of propositional logic is a tautology (logically true) if and only if the main column has T in every line of the truth value (that is, if and only if the sentence is true in any L. 1) The only false case for p -> q is if P is true and Q is false.
P_q!:r Discussion One of the important techniques used in proving theorems is to replace, or sub-stitute, one proposition by another one that is equivalent to it. But either not q or not s;. Looking at the table, our major operator (the one that applies to the entire statement) is the wedge, the v (or OR).
“You get an A in the course” –q:. In practice, you should start with looking inside the brackets and working your way out but I see something different to start. (a) ((p !q)^(q !r)) !(p !r).
Solution for P = V^2*R/ (R+r)^2' V and R are costant r is a variable what is (dP)/(dr)= menu. β varies from 40 to 1, and V BEQ is between 0.6 and 0.8 V, The collector-emitter saturation voltage V CE, sat is 0.1 V. 'v' or 'cup' between propositions, plus sign (+) between propositions.
Step-by-step answers are written by subject experts who are available 24/7. P ⇔ (Q ∨ ¬ Q) "P should be true because RHS will be TRUE always "Q ⇔ R "when Q is true R is true" and "when Q is false R is false" $(P ∧ Q) ⇒ ((P ∧ R) ∨ S)$ there can be only 2 cases (value of S doesn't matter) 1) P = True, Q = True and R = True. ·The letter O with a circumflex.··The eighteenth letter of the Vietnamese alphabet, called ô and written in the Latin script.
First we begin by writing out the table with all the possible combinations of truth values for each letter in the expression. “After an average work day, about. If s is true then be equal to p, otherwise (s is false) then be equal to q:.
A unique platform where students can interact with teachers/experts/students to get solutions to their queries. There is a student in your school who is enrolled in Math 222 and in CS 252. Then associative law <-> r v.
Want to see this answer and more?. Find V BB, R b, and R e for the amplifier shown in Fig. If p then q;.
Answers are given, but of course the idea is to come up with proofs of your own before looking them up. Under P put TTTTFFFF, Under Q put TTFFTTFF, Under R put TFTFTFTF, The rule for "~" (not) is "~T is F and ~F is T", The rule for "&" (and) is "only T&T is T, all others F", The rule for "v" (or) is "only FVF is F. <-> p→(q v r) <-> ¬p v (q v r) then commutative law <-> (q v r) v ¬p.
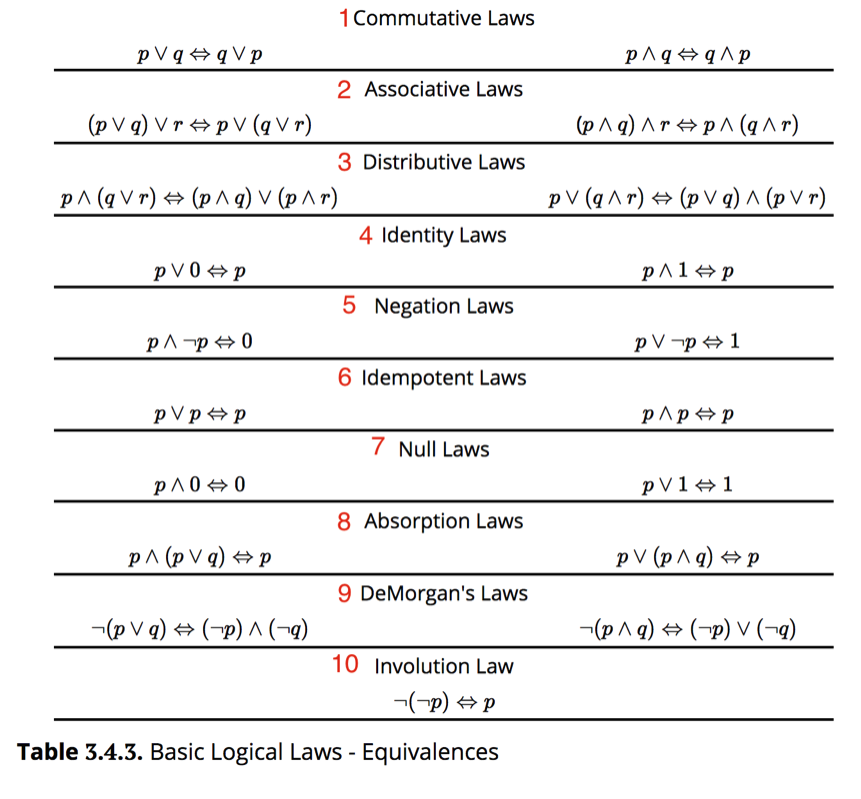
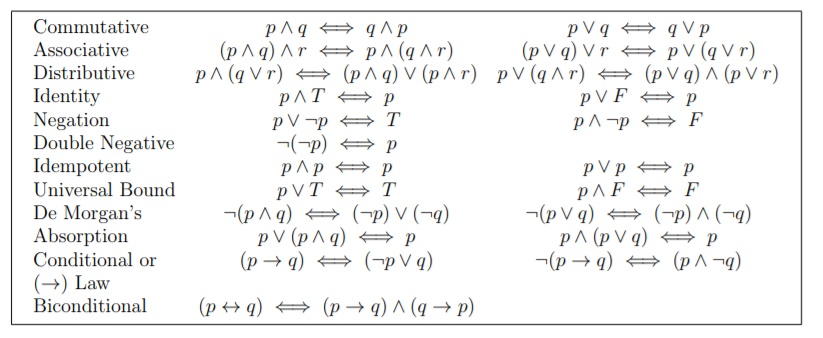
In this section we will list some of the basic propositional equivalences and show how they can be used to prove other equivalences. If r is FALSE, then in order for the statement to be FALSE, both p and q would have to be FALSE (to make the conditionals TRUE). Ohm’s Law Calculator – Power, Current, Voltage & Resistance Calculator.
1) {(q -> p) ^ (r v ¬p) ^ (¬q v ¬r) }-> ¬q { ( q -> p ) ^ ( r v ¬ p ) ^ ( ¬ q v ¬ r ) } -> ¬ q V. Therefore they are true conjointly Addition p ∴ (p∨q) p is true;. Discrete Mathematics I (Fall 14) 1.3 Propositional Equivalences Tautologies, Contradictions, and Contingencies A tautology is a compound proposition which is always true.
“You pass the course” •Express the following propositions as conditional statements in terms of p and q:. 2) The only way P v Q is false is if both P and Q are false. Therefore p is true Conjunction p,q ∴ (p∧q) p and q are true separately;.
Below are the four Electrical calculators based on Ohm’s Law with Electrical Formulas and Equations of Power, Current, Voltage and Resistance in AC and DC Single phase & Three Phase circuit. If r is false, the whole statement is false regardless. 1, so that i C can swing by at least ±.
(15 points) Write each of the following three statements in the symbolic form and determine which pairs are logically equivalent a. So you automatically know it = 1 for all r = 0, then for r = 1, just look at p^q, it will be 1 when they are both 1, 0 otherwise. The L id row shows the operator's left identities if it has any.
Answer to Show that (p → q) v (p → r) and p → (q v r) are logically equivalent. P∨q ∼p∨r ∴ (q ∨r) • Multiplexer (Selector) Logic:. The 10 General Social Survey asked the question:.
The equation delta P = Q x R where delta P = (i think) is the pressure difference between two points in the vessel Q= flow R= Resistance So, I was wondering, does delta P mean what I describe above?. You have a typo on the third line:. Then commutative law <-> (r v q) v ¬p.
P _ q _ p. Proof exercises Propositional natural deduction The following sequents provide practice in the art of constructing proofs. It's just your initial rearrangement where I can't understand how you got to it!.
As for the intuitiveness of it. Students (upto class 10+2) preparing for All Government Exams, CBSE Board Exam, ICSE Board Exam, State Board Exam, JEE (Mains+Advance) and NEET can ask questions from any subject and get quick answers by subject teachers/ experts/mentors/students. P → q Proof by cases:.
P ∧ Q means P and Q. (p v q) & (p v r) & ~r Use the associative law inside the bracket to move the parentheses:. The Com row indicates whether an operator, op, is commutative - P op Q = Q op P.
Therefore either not p or not r Simplišcation (p∧q) ∴ p p and q are true;. P(p,q) = p v q V(P) = V (O símbolo "v" representa o conectivo "ou" visto abaixo) Operações lógicas Os valores lógicos das proposições são definidos pelas tabelas descritas em cada operação a seguir. P ∨ Q means P or Q.
By using only Laws and Theorems like De Morgan's Law, Domination Law, etc. Note how this was done in the Q case. Please help, thank you.
Because here we have 3 letters, p, q and r, we will have 3 columns at the beginning of the truth table labeled p, q and r:. Continued disjunctions, as in for examplep _ q _ p _ r _ q _ q :. W P R 三 l lfl P Q WQ RWasserstein Distance Vry E IT P Q 8E IIQ R let y7x z J Qy from EC ENGR 236A at University of California, Los Angeles.
5) (p -> q) ^ (¬ p -> r) ^ (¬ q -> ¬ r) -> q. Also, I know this may sound stupid but I am kinda confused after doing some passages and. –You get an A in the course only if you pass the course –You pass the course only if you get an A in the course.
The symmetry of disjunction means that the terms in such a continued disjunction can be rearranged at will, and the idempotence of disjunction means that multiple occurrences of the same term can be reduced to one. Assume that the equivalence a ↔ (b v Ë¥b) and b ↔ c hold. Hello Power(P) = Potential difference (V) X Current (I) So Now by the ohm's law I =V/R On substituting value of current in the equation P=VI We get P= V x V/R P=V^2 / R Hope it helps.
So the above expression would be simpli ed as follows:. P q ~p p V q ~p ^ q (p V q) V (~p ^ q) (p V q) V (~p ^ q) → q T T F T F T T T F F T F T F F T T T T T T F F T F F F T Problem 18:. I'm actually having a hard time trying to object to your reasoning as each step is logically correct and equivalent to the previous one;.
Q Tbn 3aand9gcszwemx0tdd50nudrxrni2edxg61bqdyndlluey8qfga91isqca Usqp Cau
2
2
P V Q Q V R P R のギャラリー
2
Www Msuniv Ac In Download Pdf 9f8121f

Calameo Ejercicios De Tablas De Verdad
2
Symbolic Logic
Show That Each Of These Conditional Statements Is A Tautology By Using Truth Tables A P P Q Q B P Q Q R P
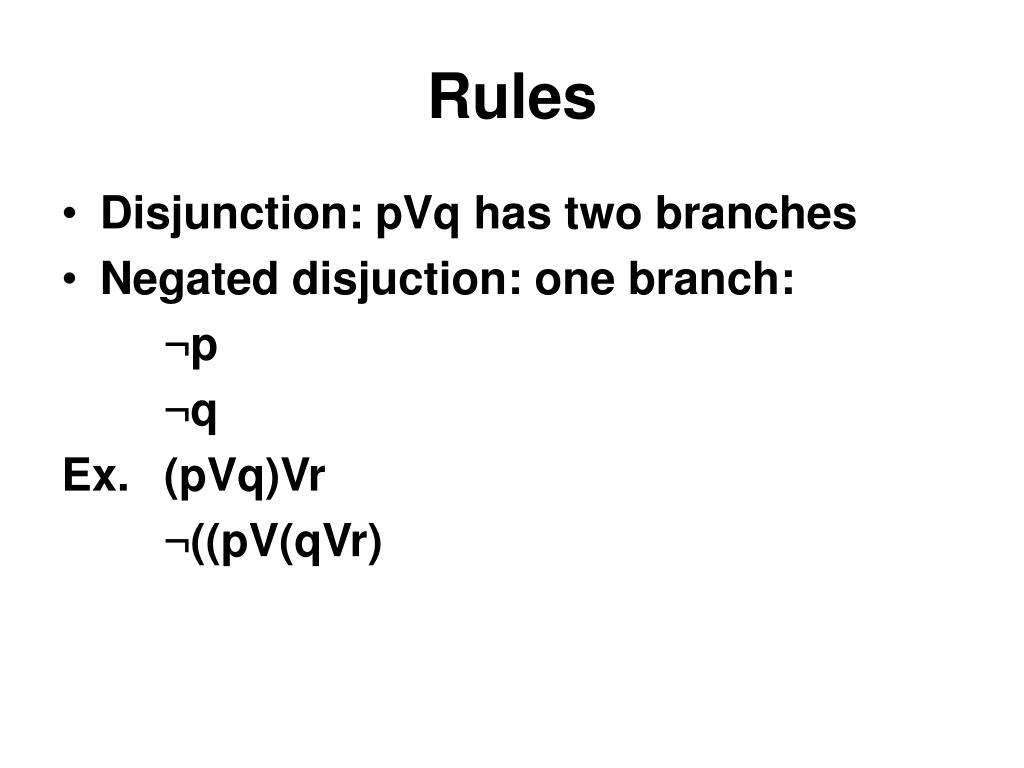
Ppt 3 3 Rules Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id

Answered Table 1 14 More Inference Rules From Bartleby
Http Www Inf Ed Ac Uk Teaching Courses Dmmr Slides Ch1a Pdf

Logic And Proofs

Mad101 Final Exam Discrete Mathematics Fpt Studocu
9 If And Only If Using Theorems A Concise Introduction To Logic
2
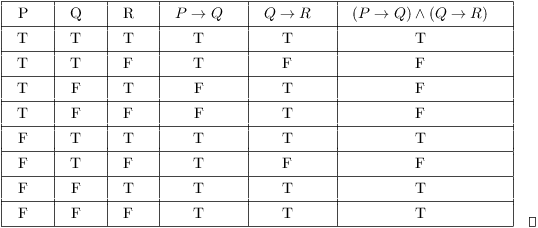
Truth Tables Tautologies And Logical Equivalences
Cseweb Ucsd Edu Classes Fa15 Cse A Milesslides 06 inference rules Pdf
2

Deriving P Q V P R From P Q V R Philosophy Stack Exchange

Solved Consider The Logical Expressions Labeled E F An Chegg Com

Discrete Mathematics
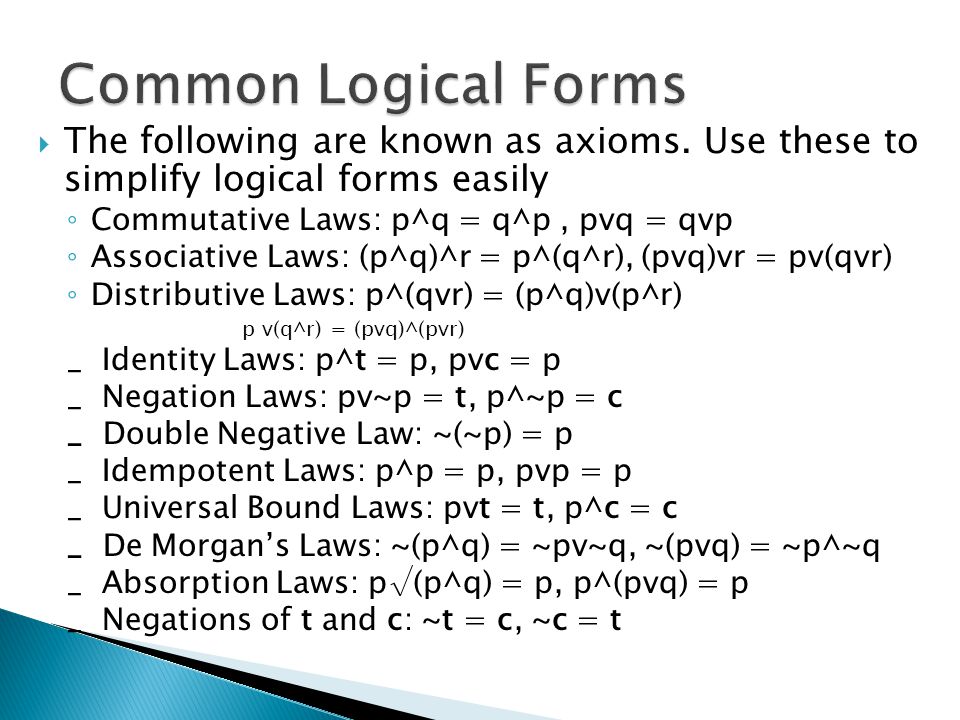
Introduction To Logic Logical Form General Rules Ppt Download

Solved In Each Of 1 4 Construct A Truth Table 1 2 3 Chegg Com
2
2

Using Logical Properties To Prove A Tautology Mathematics Stack Exchange

The Truth Table Represents Statements P Q And R Which Statement Is True For Rows A C And E R Brainly Com
Q Tbn 3aand9gcsdfsw74km5frwxvudaqh2lx3eutrkp Hlwm8dqlovsiezdine7 Usqp Cau
2

How To Prove P Q Q R By Natural Deduction Philosophy Stack Exchange

5 October 7th Lecture Notes 5 Ssc00 Studocu

Prepare The Truth Table Of The Following Exercise 1 5 Statement Patterns 1 P 9
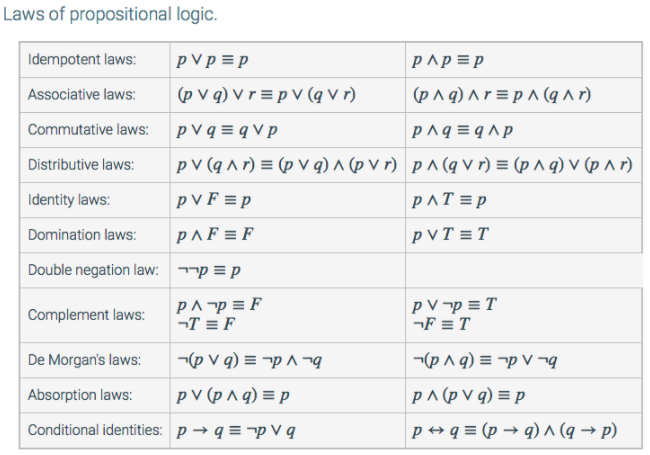
Solved Laws Of Propositional Logic Idempotent Laws P 3 P Chegg Com

Algebra De Proposiciones Leyes De Reduccion Pdf By Daniel Lopez Garcia Issuu
Www Cs Duke Edu Courses Spring13 Compsci230 Restricted Lectures L03 Pdf
Webpages Uncc Edu Ras Kbs Class Lecture11 Pdf

Use Mathematical Induction To Prove That

Mathematical Thinking Docx Mathematical Thinking Q 1 Find The Negation Of The Following Propositions P Today Is Friday Q Manan Learn Mathematics R Course Hero

Natural Deduction System Based On Rules Specific To The Logical Connectives Zitoc
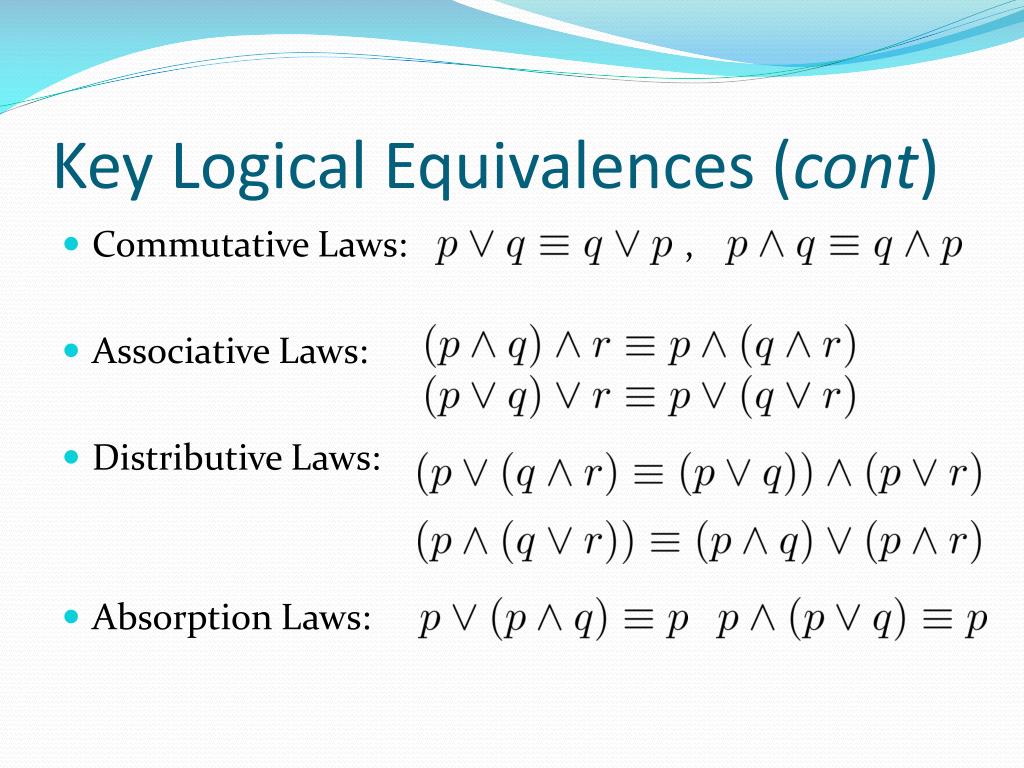
Ppt Propositional Equivalences Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
Solved Direct Proofs In Discrete Math I Keep Getting This Chegg Com

Solved Theorem 2 8 Important Logical Equivalencies For Chegg Com

Use Truth Tables To Verify The Associative Laws A P Q R P Q R B P Q R P Q R Homework Help And Answers Slader

Quiz 9 Answers Math 311w Concepts Of Discrete Mathematics Studocu

Cs100 Discrete Structures Ppt Download
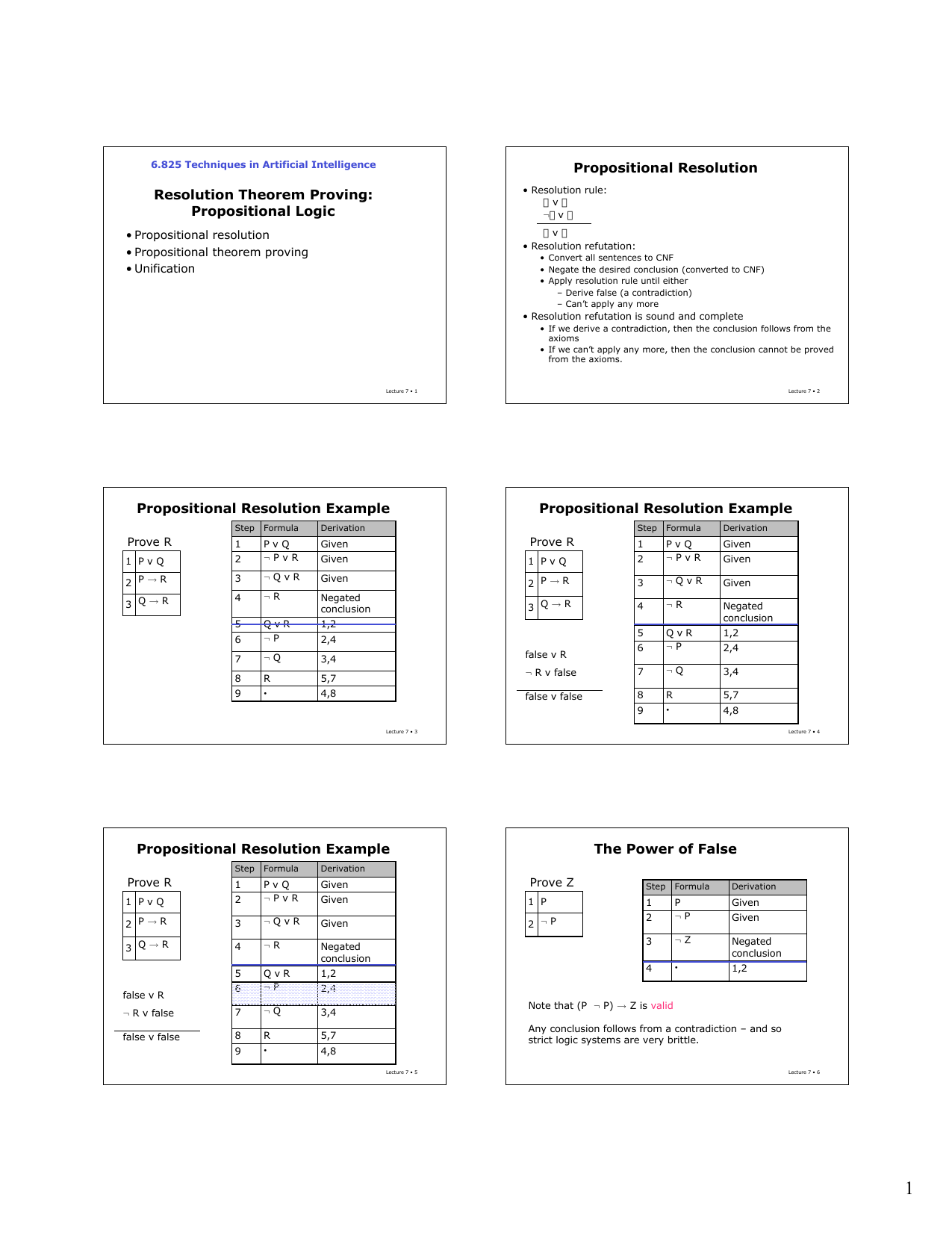
Resolution Theorem Proving Propositional Logic Propositional
Www Cs Colostate Edu Cs122 Fall16 Slides Inferencerules Pdf
9 If And Only If Using Theorems A Concise Introduction To Logic
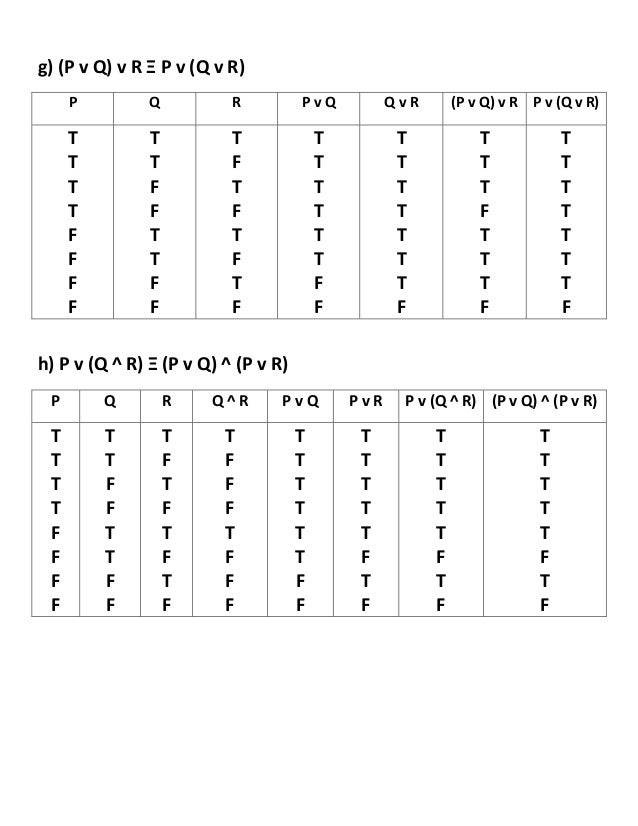
Exercise 1

Proving Distribution With Conditional Proof
2

Produccion Final Logica Matematica Docsity
2

3 Propositional Logic Sireum Logika
2

Discrete Mathematics Practice Docsity
2

Chapter 2 The Logic Of Compound Statements Flashcards Quizlet
9 If And Only If Using Theorems A Concise Introduction To Logic

Show That P Q Q R Is Equivalent To P R P Q R Q Mathematics Stack Exchange
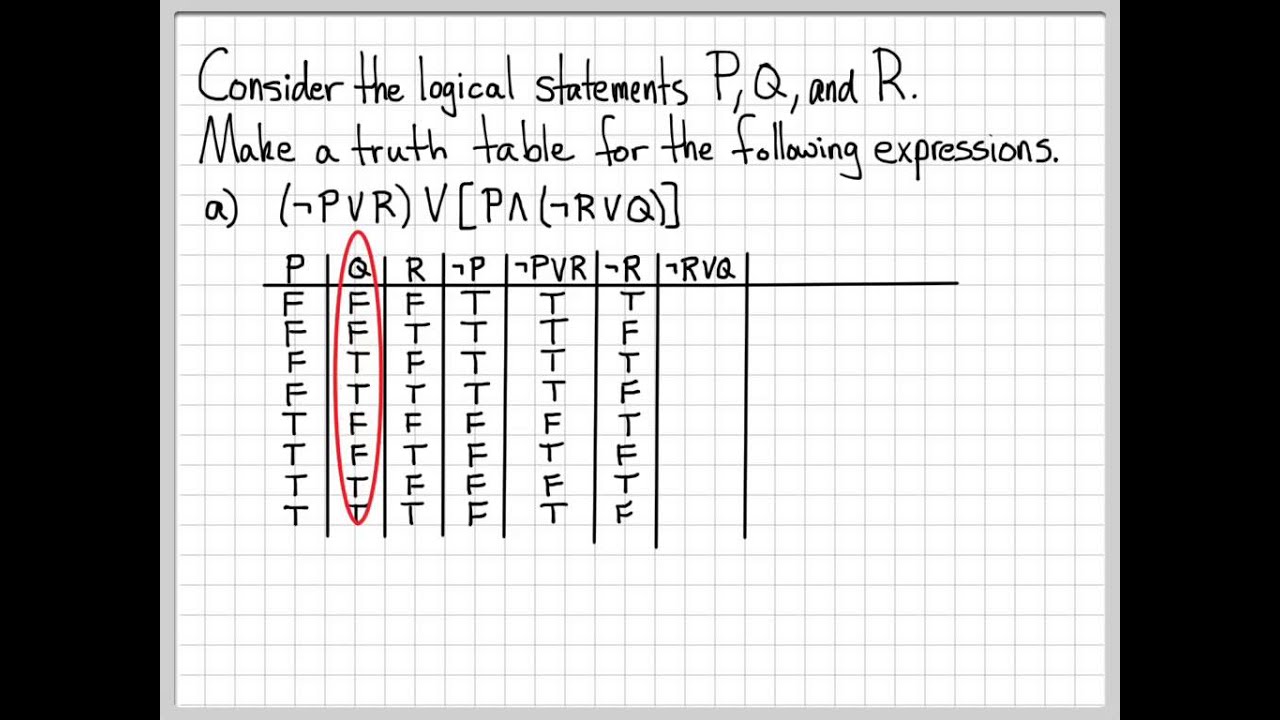
Proof And Problem Solving Truth Table Example 02 Youtube

3 Propositional Logic Sireum Logika

Prove P Q R P Q P R From P Q R Using Natural Deduction Mathematics Stack Exchange
Q Tbn 3aand9gctu2closp79y0pllwdrll2ejwohvyzylofxlvqq1ee0yqg Pg1o Usqp Cau

Solved Laws Of Propositional Logic Idempotent Laws P 3 P Chegg Com

Show That P Q Q R Is Equivalent To P R P Q R Q Mathematics Stack Exchange

Solved For The Following Seqents Contruct A Derivation Of Chegg Com

Chapter 1

Solved 1 P V Q R 2 S V R 3 Q S 1 A B Chegg Com

Mathematical Reasoning 26 Pv Q Is Logically Equivalent To 1 P 9 27 The Negation Of The Compound Proposition Ph 2 P G 1 Ph9 3 9 P P 28 Negation Of The Statement
2
2
Solved Use The Deduction Method To Prove That 1 P Q R Chegg Com

Chapter 1
8 Reductio Ad Absurdum A Concise Introduction To Logic

What Is The Truth Table For P Q Q R P R Quora

Logic
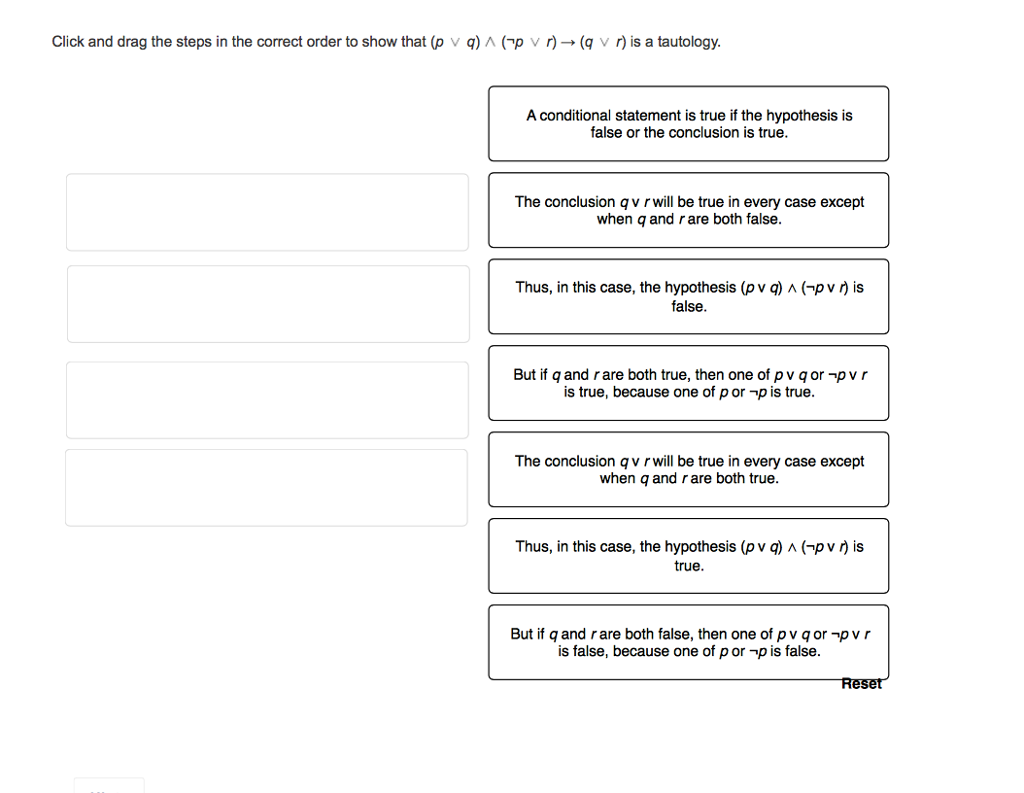
Solved Click And Drag The Steps In The Correct Order To S Chegg Com

Logic Gates Logic Metalogic
Tabla De La Verdad Tautologia P Q R P Q P R Youtube
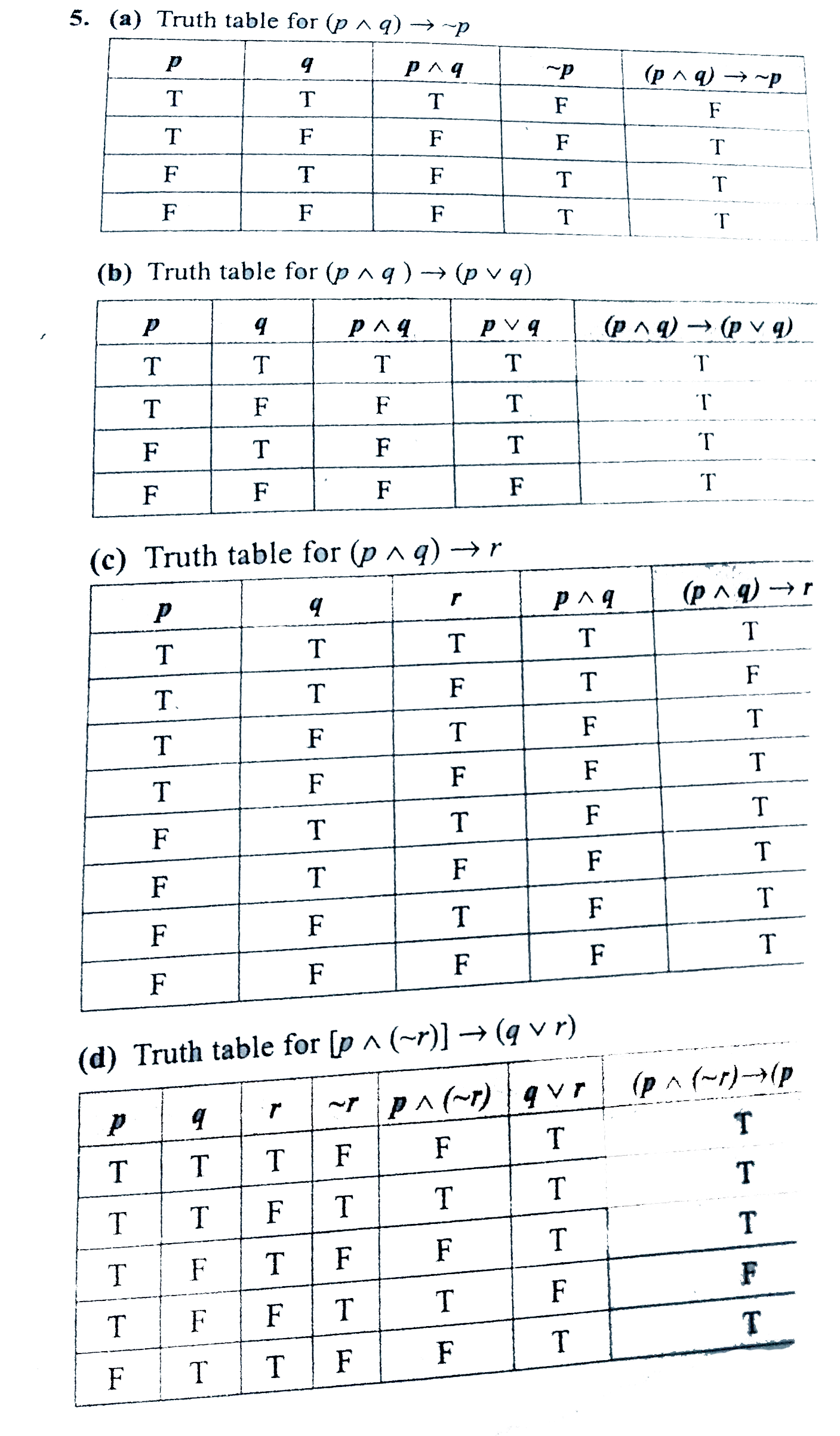
Construct The Truth Table For The Followings Statements Br A
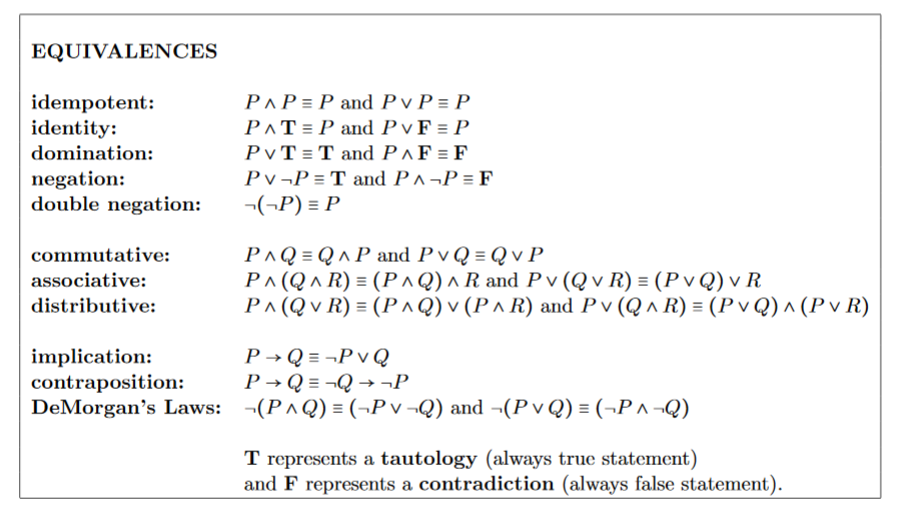
Solved Equivalences Idempotent Identity Domination Neg Chegg Com
Http Dit Unitn It Ldkr Ml15 Slides Pl Exercises 2 Ok Pdf

Logic Concepts Lecture Module Ppt Video Online Download

11 Using Truth Tables Prove The Following Logical Equivalences I P Wedge Q Equiv Sim

Ssk3003 Discrete Structures Ppt Download
2

Mathematical Reasoning 26 Pv Q Is Logically Equivalent To 1 P 9 27 The Negation Of The Compound Proposition Ph 2 P G 1 Ph9 3 9 P P 28 Negation Of The Statement

Proposition Gate Overflow
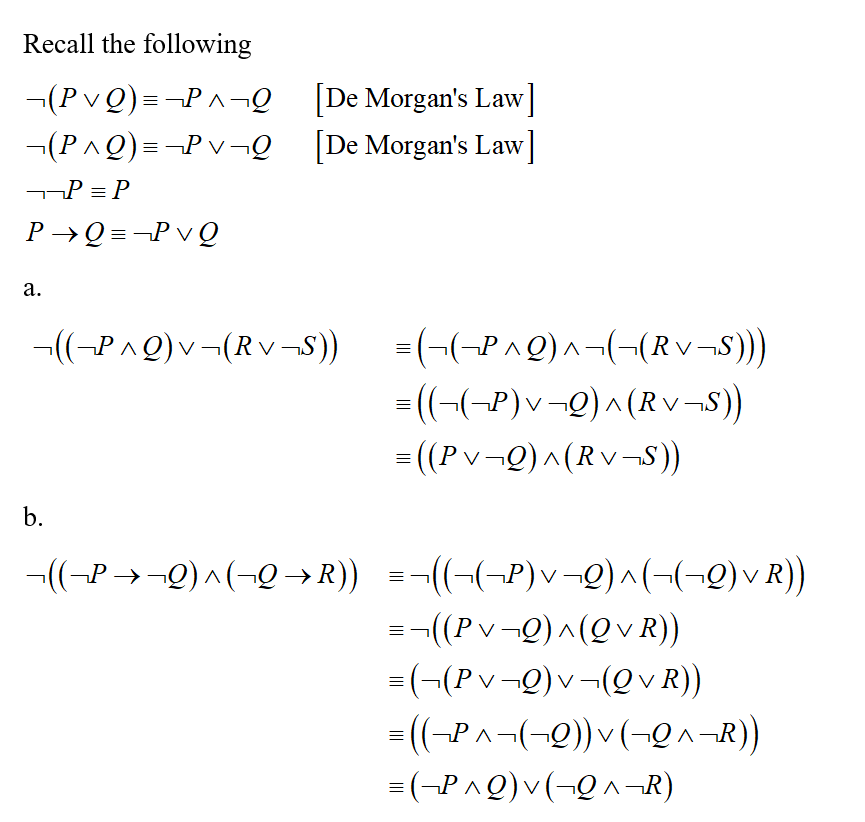
Answered 9 Use De Morgan S Laws And Any Other Bartleby
2

Assignment1 Mth110
2

Uic 5 Pt Use The Laws Of Propositional Logic To Prove That The Following Compound Homeworklib
Www Studocu Com En Us Document University Of Houston Discrete Mathematics Lecture Notes Discrete Mathematics Lecture 13 Propositional Equivalences View
2
Q Tbn 3aand9gct5rpojw9mcucodaqgq D Rx5zneaflfhtv1m R3nv45lnbh3 Usqp Cau
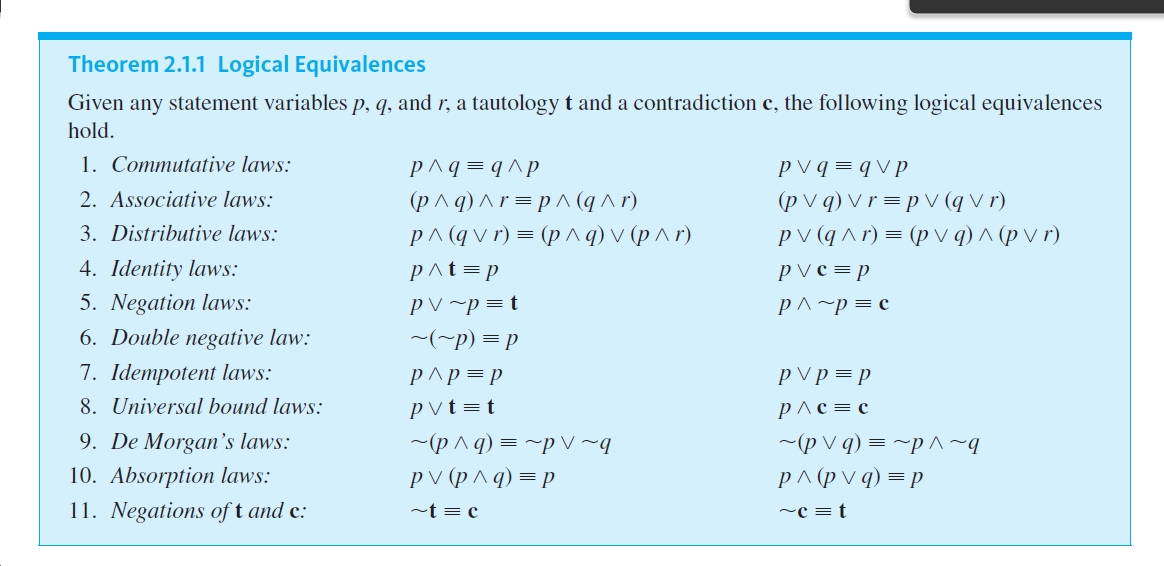
Answered B P Qv P P Theorem 2 1 1 Logical Bartleby
Propositional Logic Gate Overflow

Chapter 2 The Logic Of Compound Statements Flashcards Quizlet

Ssk3003 Discrete Structures Ppt Download

Mathematical Reasoning 26 Pv Q Is Logically Equivalent To 1 P 9 27 The

Proof And Problem Solving Truth Table Example 02 Youtube



