P Q R P Q Truth Table
Make truth table for followings:.
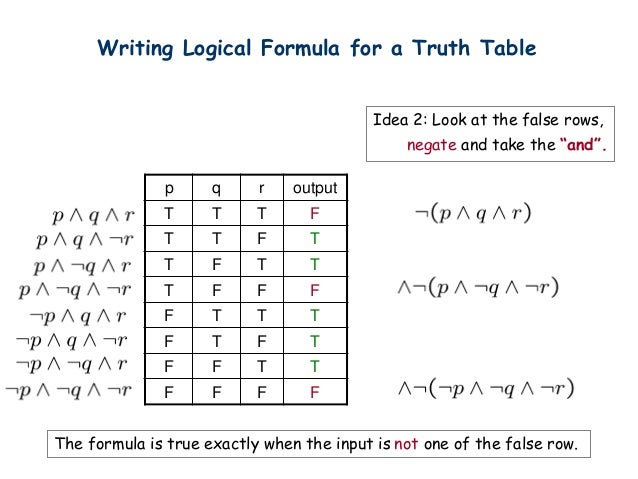
P q r p q truth table. (p $ q ). Since there are 2 variables involved, there are 2 * 2 = 4 possible conditions. Show :(p!q) is equivalent to p^:q.
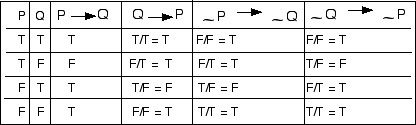
Else the statement will always be false. However, the other three combinations of propositions P and Q are false. Disjunction Truth Table ( r v p ), Or v Biconditional Truth Table ( b<-> s ) (triple bar)iff Negation Truth Table ~p Conditional Truth Table ( P⊃ Q ) P->Q if P, then Q.
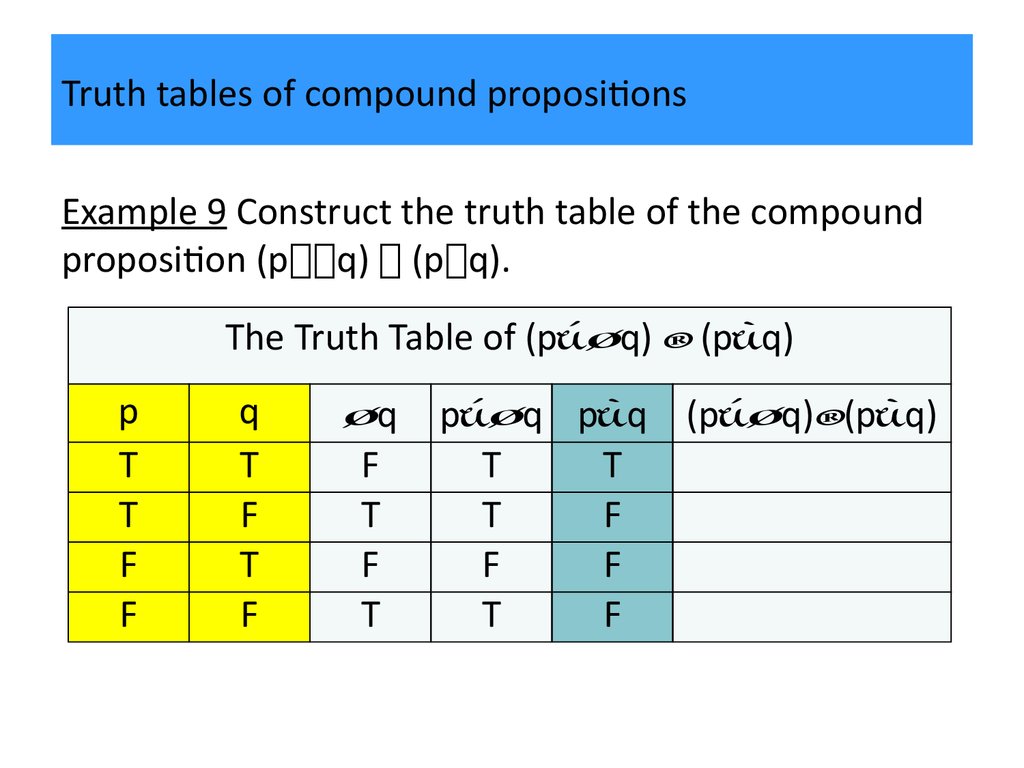
So we'll start by looking at truth tables for the five logical connectives. B) Show that (p #q) #(p #q) is logically equivalent to p^q. It’s obvious that ~ (p → q) and p ∧ ~q always share the same truth tables, so they are logically equivalent.
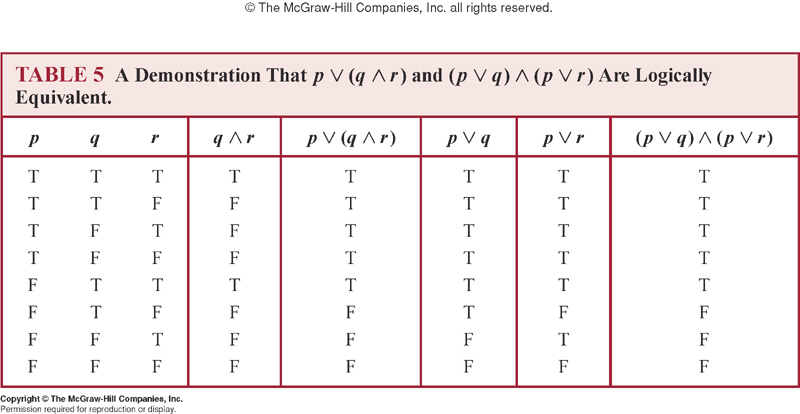
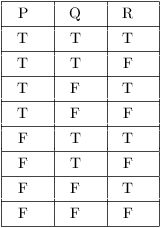
The resulting table gives the true/false values of \(P \Leftrightarrow (Q \vee R)\) for all values of P, Q and R. Suppose That A System Has 3 Inputs (P, Q, And R With P Being The Left-most Bit And R Being The Right-most Bit). Construct truth table for followings (¬ p ∨ q) ∧ (q → ¬ r ∧ ¬ p) ∧ (p ∨ r) 12.
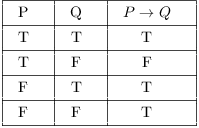
The Output (X) Of This System Is 1 When P And Q Are Opposites Of Each Other, 0 Otherwise. Then.” (In the “or” table, for example, the second line reads, “If p is true and q is false, then p ∨ q is true.”) Truth tables of much greater complexity, those with a number of. The conditional statement p q, is the proposition “if p, then q.” The truth value of p q is false if p is.
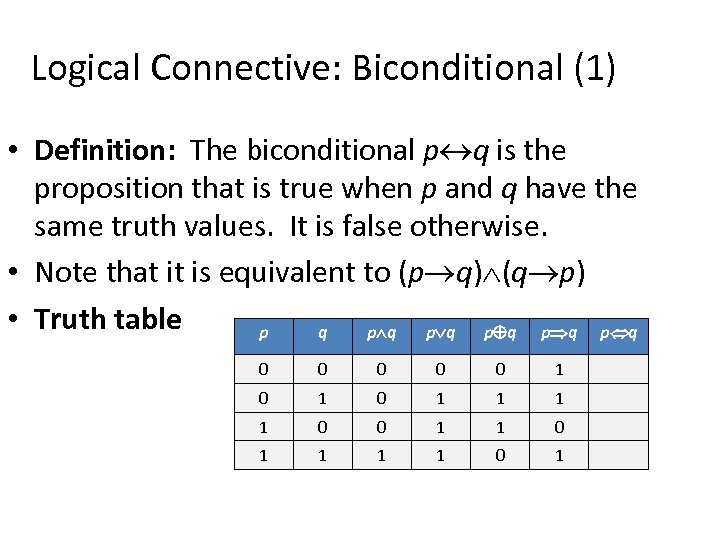
Step-by-step answers are written by subject experts who are available 24/7. Convert The Following Problem Into A Truth Table And Fill The Table Below. This is another way of understanding that "if and only if" is transitive.
Y = 0 have various truth values, but the statement \(P \Leftrightarrow (Q \vee R)\) is always true. I, B number of lines. Conditional If p then q p→q Converse If q then p q→p Inverse If ∼p then ∼q ∼p→∼q.
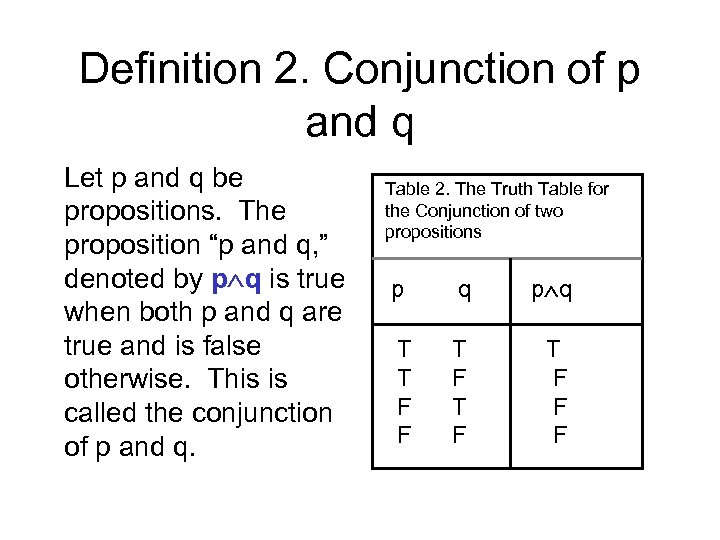
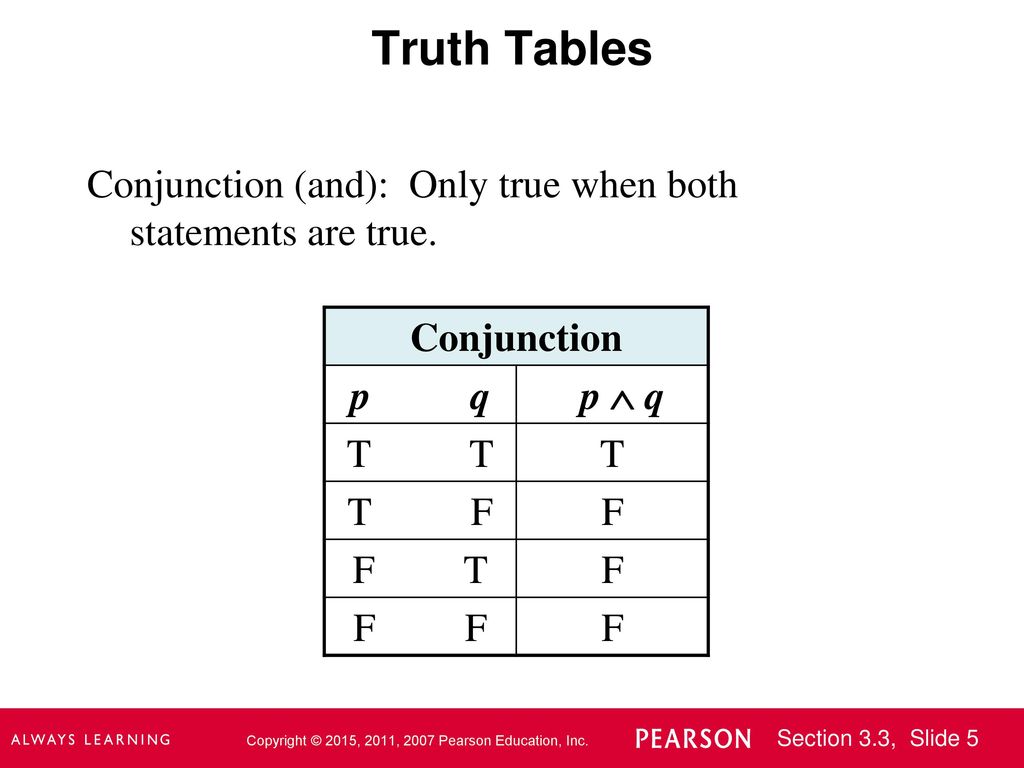
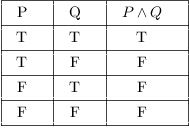
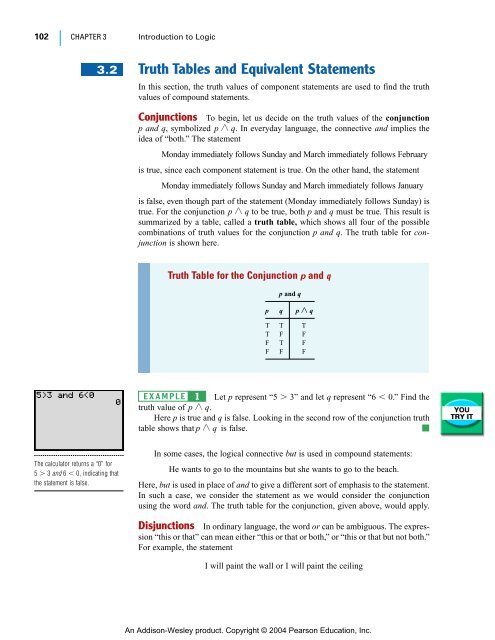
In the first column for the truth values of \(p. A truth table has one column for each input variable (for example, P and Q), and one final column showing all of the possible results of the logical operation that the table represents (for example, P XOR Q). The statement contains 'and', so the statement will be true when both the statements are true.
↓ I, A variables in alphabetical order ↓ III, A First line all T → p:. P q r p → q p∨ r r → T T T T T T → T T F T T F T F T F T T T F F F T F → F T T T T T F T F T F F → F F T T T T F F F T F F This is clearly not a valid argument - as stated above, if the victim had money in their pockets, and the motivation of the crime was robbery. In this case, that would be p, q, and r, as well as:.
C) Since problem 44 shows that :and ^form a func-tionally complete collection of logical operators, and each of these can be written in terms of #, therefore #by itself is a. Truth tables for compounds of great complexity having more than one truth functional operator can be constructed by computers. The conditional p ⇒ q can be expressed as p ⇒ q = ~p + p Truth table for conditional p ⇒ q For conditional, if p is true and q is false then output is false and for all other input combination it is true.
P → ( q → r ) and ( p → q ) → r p q r p → q q → r p → ( q → r ) ( p → q ) → r T T T T T T T T T F T F F F T F T F T T T T F F F T T T. The NOR operator is also known as Peirce's arrow—Charles Sanders Peirce introduced. This is just the truth table for P → Q, P → Q, but what matters here is that all the lines in the deduction rule have their own column in the truth table.
Symbols used for exclusive-or include a circled plus sign, an equivalence sign with a slash (/) through it (read 'p not equivalent to q'), or sometimes a circled 'v'. The truth or falsity of P → (Q∨ ¬R) depends on the truth or falsity of P, Q, and R. The truth table has 4 rows to show all possible conditions for 2 variables.
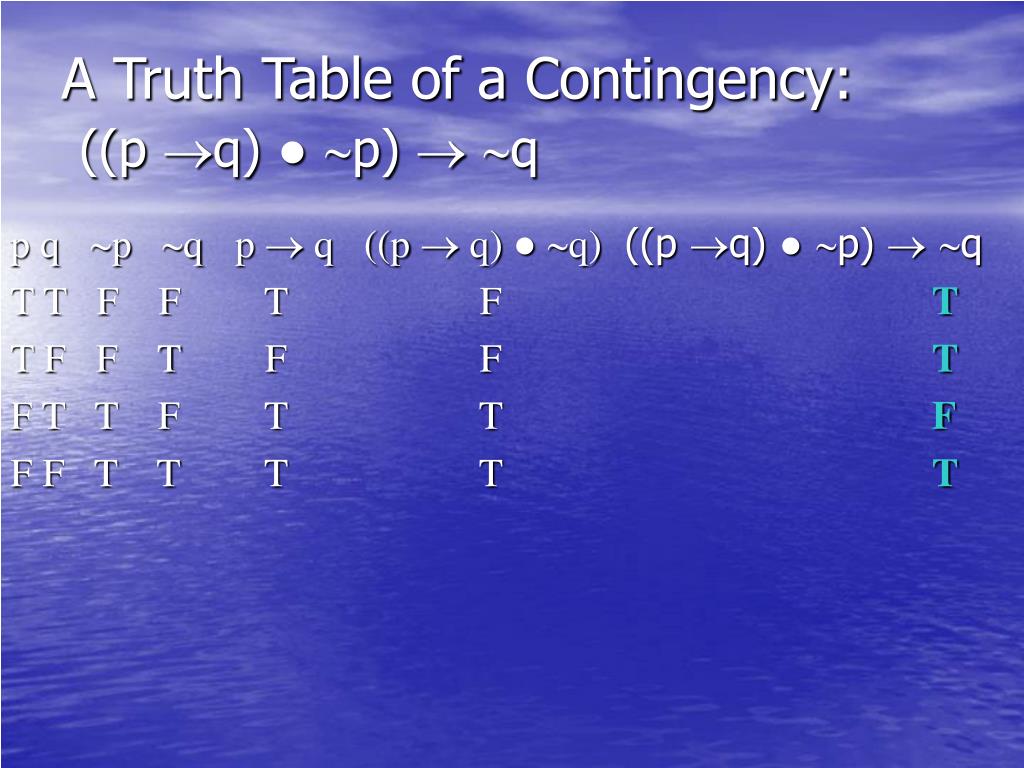
Xy = 0, Q:. + an = rwhere r is a. Construct a truth table for "if (P if and only if Q) and (Q if and only if R), then This will always be true, regardless of the truths of P, Q, and R.
Each row of the truth table contains one possible configuration of the input variables (for instance, P=true Q=false), and the result of the operation for those values. We can also express conditional p ⇒ q = ~p + q Lets check the truth table. Remember that an argument is valid provided the conclusion must be true given that the premises are true.
P q :q p!q :(p!q) p^:q T T F T F F T F T F T T F T F T F F F F T T F F Since the truth values for :(p!q) and p^:qare exactly the same for all possible combinations of truth values of pand q, the two propositions are equivalent. Construct the truth table for the statements (pVq) V (~p^q) → q p q ~p p V q ~p ^ q (p V q) V (~p ^ q) (p V q) V (~p ^ q) → q T T F T F T T T F F T F T F F T T T T T T F F T F F F T Problem 18:. A truth table lists all possible combinations of truth values.
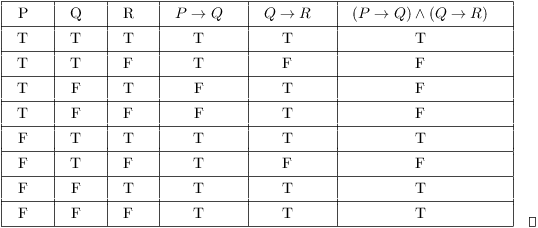
We start by listing all the possible truth value combinations for A , B , and C. (3 Marks) i) p→ (~ q ∨ ~ r) ∧ (p ∨ r) ii) p→ (~ r ∧ q) ∧ (p ∧ ~ q). Use a truth table to show that \(p \wedge q) \Rightarrow r \Rightarrow \overline{r} \Rightarrow (\overline{p} \vee \overline{q})\ is a tautology.
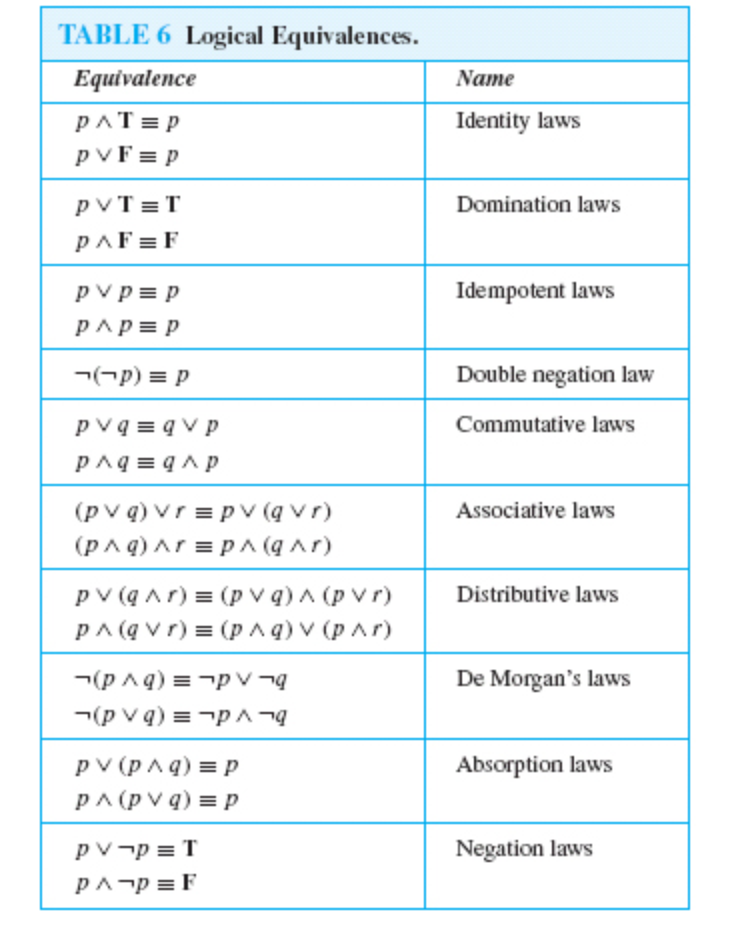
Want to see this answer and more?. The truth table is:. Table of Logical Equivalences Commutative p^q ()q ^p p_q ()q _p Associative (p^q)^r ()p^(q ^r) (p_q)_r ()p_(q _r) Distributive p^(q _r) ()(p^q)_(p^r) p_(q ^r) ()(p_q.
~(p ^ q) V (p V q) - Answered by a verified Tutor. The truth or falsity of depends on the truth or falsity of P, Q, and R. A) Show that p #p is logically equivalent to :p.
Construct the truth table for the following compound proposition. Find the number of non-negative integer solutions of the equation:a1 + a2 +. P q p q T T T T F F F T F F F F 14.
Truth Table •The truth table for p q is as follows:. Truth Table Generator This tool generates truth tables for propositional logic formulas. Discrete Mathematics I (Fall 14) d (p^q) !(p !q) (p^q) !(p !q) :(p^q)_(p !q) Law of Implication :(p^q)_(:p_q) Law of Implication.
3 Points In The Following Truth Table P, Q, And R Are Inputs And X Is The Output. This principle can proved another way as well:. X = 0 and R:.
Is used often in CSE. When both of p and q are false.In grammar, nor is a coordinating conjunction. P q is the same as :.
Otherwise, P \wedge Q is false. The number of rows in this truth table will be 4. Notice that when we plug in various values for x and y, the statements P:.
A truth table is a way to visualize all the possibilities of a problem. Number of solutions of a1+a2. A) Use truth tables to verify the following logical equivalences.
Again, a truth table is the simplest way. Write a truth table for:. The table for “p or q” would appear thus (the sign ∨ standing for “or”):.
(Since p has 2 values, and q has 2 value.) For p ^ q to be true, then both statements p, q. The are 2 possible conditions for each variable involved. Now, our final goal is to be able to fill in truth tables with more compound statements which have more than just one logical connective in them.
In a two-valued logic system, a single statement p has two possible truth values:. If you already know that "ifthen" is. A sentence of the language of propositional logic is a tautology (logically true) if and only if the main column has T in every line of the truth value (that is, if and only if the sentence is true in any L.
Knowing truth tables is a basic necessity for discrete mathematics. Here, we will find all the outcomes for the simple equation of ~p Λ q. It helps to work from the inside out when creating truth tables, and create tables for intermediate operations.
P q r p !q p !r A q ^r B T T T T T T T T T T F T F F F F. Truth (T) and falsehood (F).Given two statements p and q, there are four possible truth value combinations, that is, TT, TF, FT, FF.As a result, there are four rows in the truth table. We list the truth values according to the following convention.
We can see that the result p ⇒ q and ~p + q are same. Conditional Statement Let p and q be propositions. Notice how the first column contains 4 Ts followed by 4 Fs, the second column contains 2 Ts, 2 Fs, then repeats, and the last column alternates.
Determine whether the following statement forms are logically equivalent. Here's the table for negation:. A)Table of truth We show that the two statements A = (p !q)^(p !r) and B = p !(q ^r) have the same truth values:.
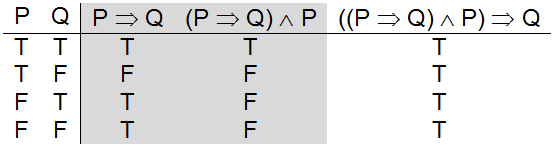
In the two truth tables I've created above, you can see that I've listed all the truth values of p, q and r in the same order.This is so that I can compare the values in the final column in the two truth tables without worrying about whether or not I am matching up the right rows - because the rows are already in the same order, I can just compare the final column of one table with the final. The truth value of the compound statement P \wedge Q is only true if the truth values P and Q are both true. The premises in this case are P → Q P → Q and P.
Show that each conditional statement is a tautology without using truth tables b p !(p_q) p !(p_q) :p_(p_q) Law of Implication (:p_p)_q Associative Law T_q Negation Law T Domination law 2. In which · signifies “and” and ⊃ signifies “if. This shows that “p or q” is false only when both p and q are false.
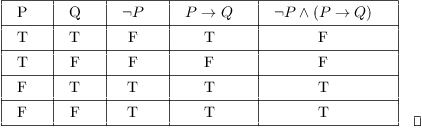
Now the statement p ∧ (r → ~ q) is calculated. Statements like q→~s or (r∧~p)→r or (q&rarr~p)∧(p↔r) have multiple logical connectives, so we will need to do them one step at a time using the order of operations we defined at the beginning of this lecture. Ø(P →(Q →R)) →(P ∧ Q →R) Using a partial truth table I will šnd out whether (P → (Q → R)) → (P ∧Q → R) is a tautology.
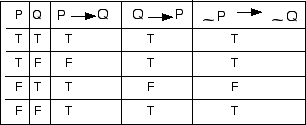
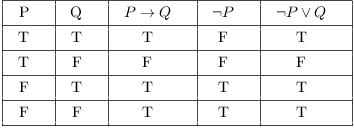
Its truth table is the opposite of the equivalence truth table (i.e. P→ q ≡¬p∨q by the implication law (the first law in Table 7.) ≡q∨(¬p) by commutative laws ≡¬(¬q)∨(¬p) by double negation law. Build a truth table containing each of the statements.
(0 points), page 35, problem 18. Questions are typically answered within 1 hour.* Q:. Construct a truth table for p ( q r ) Line No.
We need eight combinations of truth values in \(p\), \(q\), and \(r\). \(p \vee q\) \(\neg r\). (15 points) Write each of the following three statements in the symbolic form and determine which pairs.
Set up your table. \begin{array}{ccc|cccc|c} p & q & r & \neg p & \neg q & \neg p \leftrightarrow \neg q & q \leftrightarrow r & (\neg p \leftrightarrow \neg q) \leftrightarrow (q \leftrightarrow r) \\\hline T & T & T & F & F & T & T. Notice in the truth table below that when P is true and Q is true, P \wedge Q is true.
\(\left(p \vee q\right) \wedge \neg r\) Step 1:. You can enter logical operators in several different formats. Math\begin{array}{ccc|ccccccccccccccc}p&q&r&p \supset q&q\supset r&(p \supset.
The logical properties of the common connectives may be displayed by truth tables as follows:. The main ones are the following (p and q represent given propositions):. Connectives are used for making compound propositions.
In this video, we set up a truth table for the given compound statement. I discuss how to determine the truth values of the components (number of rows) and h. A truthtableshows how the truth or falsity of a compound statement depends on the truth or falsity of the simple statements from which it’s constructed.
~(p v q) is the inverse of (p v q) if a variable is true, then "not" that variable is false. Truth table for Exclusive Or p q p q T T F T F T F T T F F F Actually, this operator can be expressed by using other operators:. Just use a truth table.
The outputs are F T T F when the tables are written as above). Use either a truth table or logical equivalence to show that (p !q) ^(p !r) ,p !(q ^r) We will use a table of truth and logical equivalence:. •How about p q and p q?.
What is the truth table for (p->q) ^ (q->r)-> (p->r)?. You need to have your table so that each component of the compound statement is represented, as well as the entire statement itself. P Q R X 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 0.
A truth table shows how the truth or falsity of a compound statement depends on the truth or falsity of the simple statements from which it's constructed. Name Represented Meaning Negation ¬p “not p” Conjunction p∧q “p and q” Disjunction p∨q “p or q (or both)” Exclusive Or p⊕q “either p or q, but not both. In boolean logic, logical nor or joint denial is a truth-functional operator which produces a result that is the negation of logical or.That is, a sentence of the form (p NOR q) is true precisely when neither p nor q is true—i.e.
For example, the propositional formula p ∧ q → ¬r could be written as p /\ q -> ~r, as p and q => not r, or as p && q -> !r. Information in questions, answers, and other posts on this site ("Posts") comes from individual users, not JustAnswer;. Let p, q, r denote primitive statements.
So we have a symbol for it. Note that since the statement p could be true or false, we have 2 rows in the truth table. Here is another example of a truth table, this time for $(\neg p \leftrightarrow \neg q) \leftrightarrow (q \leftrightarrow r)$:.
JustAnswer is not responsible for Posts.

Cpcs222 Discrete Structures I Ppt Download
Ppt Philosophy 150 Day 12 Using Truth Tables Part 1 Powerpoint Presentation Id
Solved Show That Q P P Q Is A Tautology I E Q Chegg Com
P Q R P Q Truth Table のギャラリー
The Normal Genius Truth Tables

Abcd Truth Table Worksheet Printable Worksheets And Activities For Teachers Parents Tutors And Homeschool Families

The Normal Genius Truth Tables

M02 1 13 1 Consider The Statement If A Figure Is A Square 1 Consider The

In The Truth Table For The Statements P To Q Harr P Vvq T

Negative Statements Ck 12 Foundation
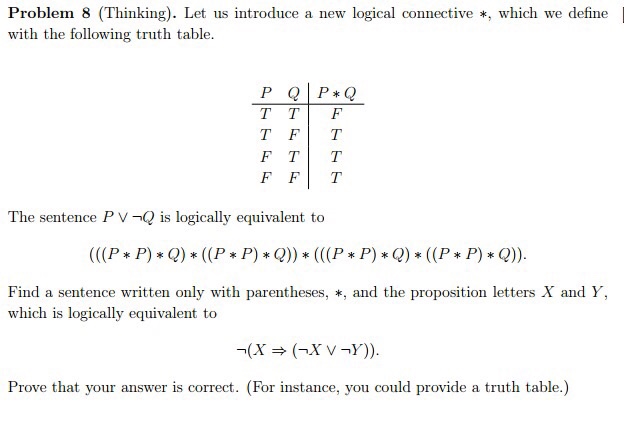
Solved Problem 8 Thinking Let Us Introduce A New Logic Chegg Com
Logic Propositions
2

Abcd Truth Table Worksheet Printable Worksheets And Activities For Teachers Parents Tutors And Homeschool Families
Solved Construct A Truth Table For The Given Statement P Chegg Com

Propositional Logic A Proposition Is A Declarative Sentence A Sentence That Declares A Fact That Is Either True Or False But Not Both Pdf Free Download
Propositional Logic Prezentaciya Onlajn

Solution How Do You Write A Truth Table For The Statement Form P Q V Pvq
2
Www Uplifteducation Org Cms Lib Tx Centricity Domain 291 Logic Practice 18 key Pdf
Propositional Logic Proposition A Proposition Is A

Watson
2
2
Solution To Example 1

Truth Tables On Ti Nspire Cx Math Tables On Ti Nspire Cx We Use 1 For T And 0 For F To Create The Truth Table Pq P Q Pq
The Normal Genius Truth Tables
Philosophy Into To Logic Brooke Byun
Truth Tables Tautologies And Logical Equivalences
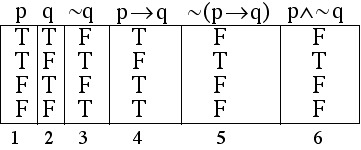
Negation

Logic Truth Tables Worksheet Printable Worksheets And Activities For Teachers Parents Tutors And Homeschool Families

Solved Use Truth Tables To Prove B C D E F G H And I Chegg Com
Propositional Logic Prezentaciya Onlajn

Dm1
Unit 1 Mathematical Logic Introduction Logic We

Boolean Tables Worksheet Printable Worksheets And Activities For Teachers Parents Tutors And Homeschool Families

Logic Easing The Hurry Syndrome

Abcd Truth Table Worksheet Printable Worksheets And Activities For Teachers Parents Tutors And Homeschool Families

Logic Truth Tables Worksheets Printable Worksheets And Activities For Teachers Parents Tutors And Homeschool Families

Truth Table For Compound Statements Youtube
Truth Tables Tautologies And Logical Equivalences
Q Tbn 3aand9gcr2oxnmnlu9pdclqvbtg6glfskyfgzj1 Hn4uchqb7nttyoluij Usqp Cau

Logic Truth Tables Worksheets Printable Worksheets And Activities For Teachers Parents Tutors And Homeschool Families

M02 1 13 1 Consider The Statement If A Figure Is A Square 1 Consider The
Truth Tables Tautologies And Logical Equivalences

Truth Value Logic Britannica

Dm1
Watson

Truth Tables Pdf Contradiction Syntax Logic

Pvq Q P Pv 7 Fill In The Truth Table For The Statement Below Homeworklib
Q Tbn 3aand9gctl2zcptshv3iyzy8meoqsjchgvcibdk4dy7nnneafmqmi2cwbv Usqp Cau
Truth Tables Tautologies And Logical Equivalences

The Foundations Logic And Proof Sets And Foundations Propositions A Proposition Is A Declarative Sentence That Is Either True Or False But Not The Ppt Download
Propositional Logic Proposition A Proposition Is A

Truth Tables For Compound Statements Youtube

Simplify Equivalent For P Q P Q Mathematics Stack Exchange
Chapter 3 Logic Ppt Download

Truth Table

Proof And Problem Solving Truth Table Example 01 Youtube

Solved Construct A Truth Table For The Statement P Q Chegg Com
Www3 Cs Stonybrook Edu Pfodor Courses Cse215 L03 Propositionallogic Pdf

Part A 5 Points Fill In The Truth Table For P Chegg Com
Www Studocu Com En Nz Document Islamic University Of Technology Discrete Mathematics Other Discrete Math Solution K Rosen7e View
Www Uplifteducation Org Cms Lib Tx Centricity Domain 291 Logic practice problems key Pdf
Http Storm Cis Fordham Edu Zhang Cs2100 Slides Logic Handout Pdf
Truth Tables Tautologies And Logical Equivalences

Chapter 1 Use The Following To Answer Questions 1 5 In The Questions Below Determine Whether The Proposition Is True Or False Pdf Free Download

Truth Table Youtube
Logical Connectors Truth Tables By Adam Sullivan

Truth Tables Pdf Contradiction Syntax Logic
Truth Table Generator Pypi
Ppt Logical Form And Logical Equivalence Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
Www Uplifteducation Org Cms Lib Tx Centricity Domain 291 Logic practice problems key Pdf

Mathematical Logic Part 2
Q Tbn 3aand9gcrrfsogu1iqmpiv56dv5oa B Pi06bmmekjofsoz Uze Prhwzl Usqp Cau
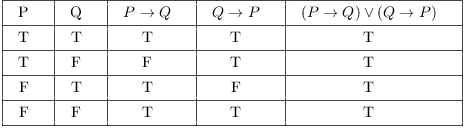
Truth Tables Tautologies And Logical Equivalences
2
Q Tbn 3aand9gctu2closp79y0pllwdrll2ejwohvyzylofxlvqq1ee0yqg Pg1o Usqp Cau

Table 2 From Two Results On Zfc 1 If Zfc Is Consistent Then It Is Deductively Incomplete 2 Zfc Is Inconsistent Semantic Scholar

2 Construct The Truth Tables For The Following Propositions 1 P P Q 2 P Q Q P 3 P Q R 4 P Q P R 3 Refer To The Propositions In Problem 2 For Each Of Them Indicate Whether It Study Com
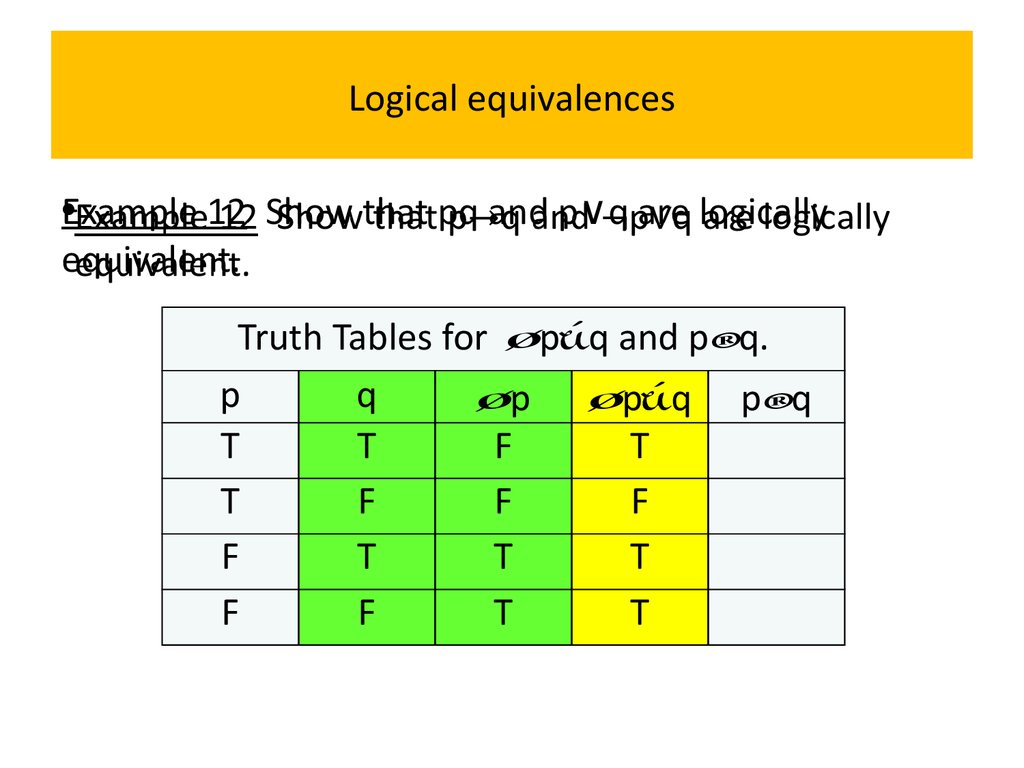
Propositional Logic Prezentaciya Onlajn

Prepare The Truth Table Of The Following Statement Patterns I P Q Q P Ii P Q P Iii P Q P Q Iv P R Q P V P Q R P

Dm1
Http Eng Usf Edu Hady Courses Mgf1106 Documents Slides 3 3 Pdf

Lecture Notes In Discrete Mathematics Marcel B Finan Arkansas Tech University C All Rights Reserved Pdf Free Download

Logic Easing The Hurry Syndrome

Propositional Logic Foundations Of Logic Overview Propositional Logic Basic Definitions 1 1 Equivalence Rules Derivations 1 2 Ppt Download

Undefined Control Sequence In A Table Tex Latex Stack Exchange

Logic Truth Tables Worksheet Printable Worksheets And Activities For Teachers Parents Tutors And Homeschool Families

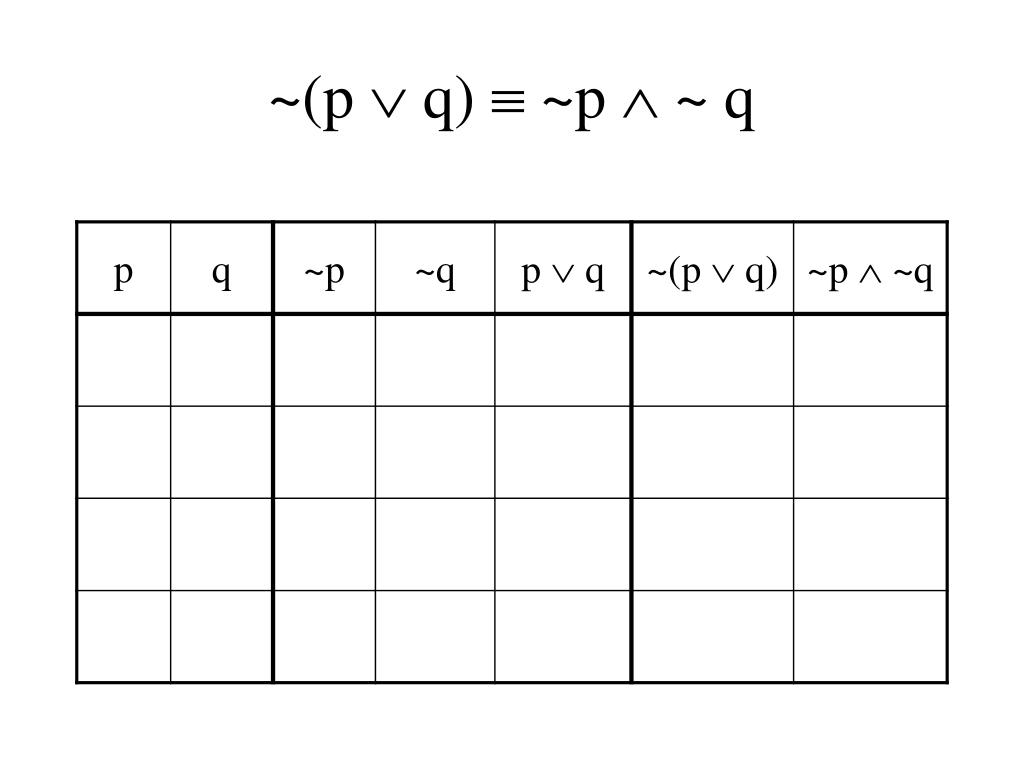
Prove That Neg P Wedge Q Leftrightarrow Neg P Vee Neg Q Using Truth Table Mathematics Stack Exchange

Truth Table Docx Partial Credit 3 2 66 A Construct A Truth Table For The Compound Statement Left Parenthesis Q Logical And P Right Parenthesis Logical Course Hero
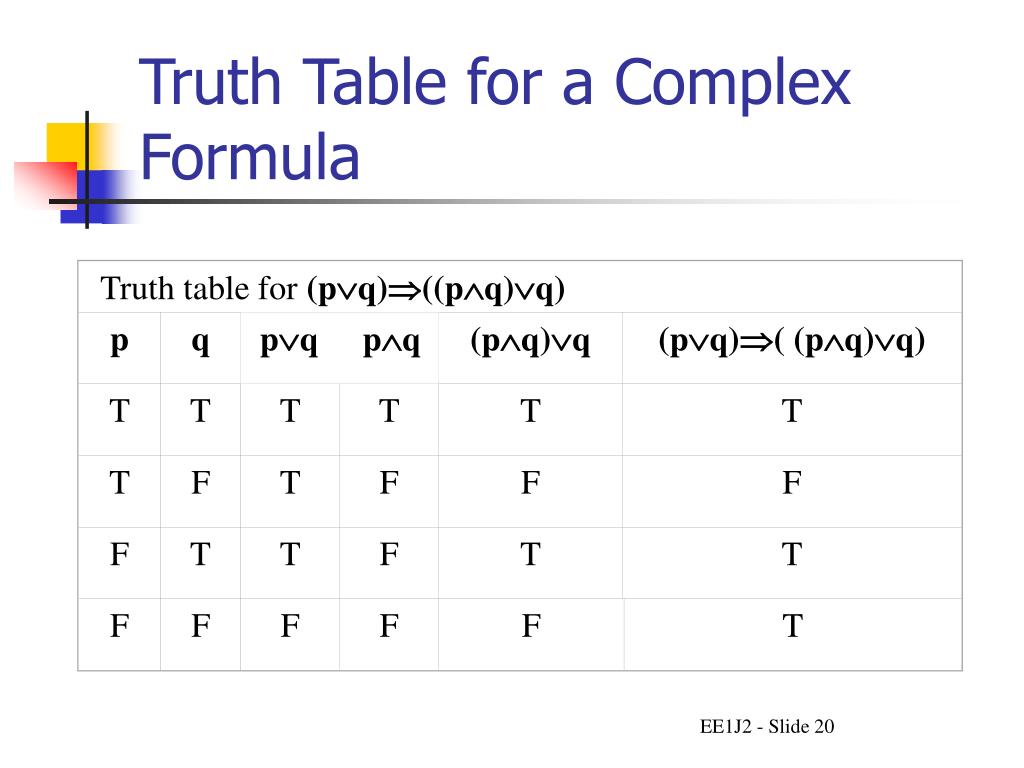
Ppt Ee1j2 Discrete Maths Lecture 3 Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id

Watson

Logic Truth Tables Worksheet Printable Worksheets And Activities For Teachers Parents Tutors And Homeschool Families

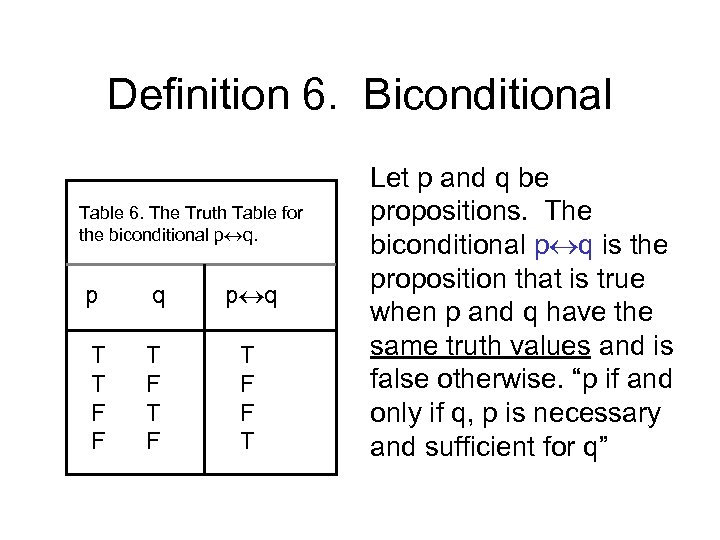
Iff Truth Table
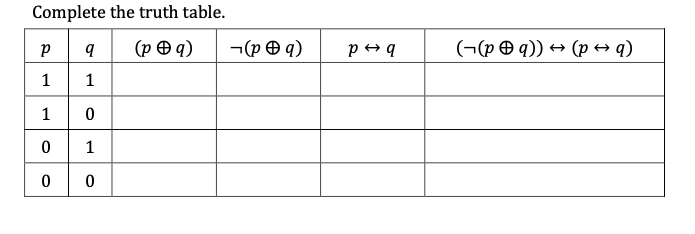
Solved Complete The Truth Table Pa P 9 1 1 9 Pa P Chegg Com
Truth Tables Tautologies And Logical Equivalences
Www Studocu Com En Nz Document Islamic University Of Technology Discrete Mathematics Other Discrete Math Solution K Rosen7e View

8 6 Testing Argument Validity Using Truth Tables Pages 1 3 Text Version Fliphtml5

50 P Q P Q P Q P Q De Morgans Laws The Truth Table For P Q P Q Theorem For Course Hero

Logic Truth Tables Worksheets Printable Worksheets And Activities For Teachers Parents Tutors And Homeschool Families

P Q P Q Prove Contradiction

Truth Tables On Ti Nspire Cx Math Tables On Ti Nspire Cx We Use 1 For T And 0 For F To Create The Truth Table Pq P Q Pq

Tautology In Math Definition Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
Truth Tables And Equivalent Statements



